Did you know there is a way to communicate directly with Google’s search engine algorithm? It’s true. Setting up a sitemap for your website is the best way to create a reciprocal relationship between your website and the SERPS. Below, is everything you need to know about creating a sitemap using SEO best practices.
Sitemap Basics
In the most basic of terms, a sitemap (also known as an XML sitemap) is a list of all website pages contained within the domain. XML is an abbreviation for extensible markup language, which is a way to communicate information on a page (just like html). In this case, the information you’re looking to share is separated into two primary display options.
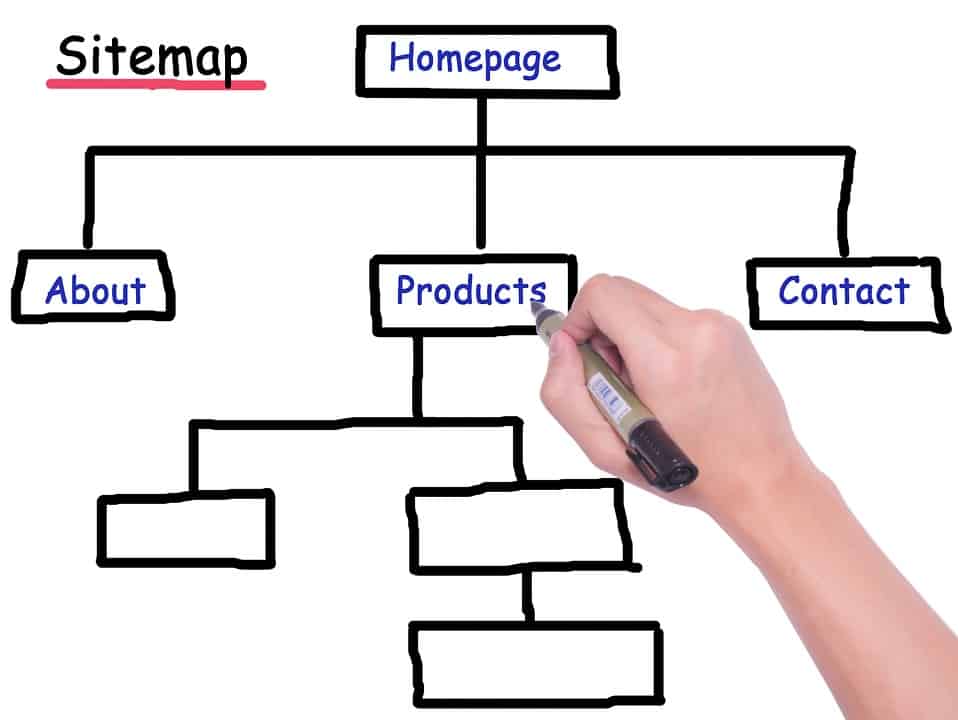
Set Up Sitemap
- First, a page will need to be created for the search engine crawlers to identify all pages that should be indexed and searchable to potential users. This is generally done using XML language and creating a page that appends “/sitemap.xml” to the end of the domain URL (i.e. com/sitemap.xml).
- The second page to create is generally more easily readable to the human eye and is simply an organized list of the same pages included in the sitemap above. Typically, this page would be accessible via a link in the footer and would include the most important areas of the website segmented by category or topic. The URL would be similar to any other page on your site (i.e. com/sitemap).
Does Having a Well-Structured Sitemap Matter?
Organizing your sitemap and making it accessible is one of the most fundamental SEO practices. Search engines rely on sitemaps to deliver the most appropriate, high-quality content to a user that makes a search query. If you intend to be found in organic search results, you must properly inform search engines (like Google or Bing) of individual page content as well as its importance relative to the entire domain.
Some websites may have tens of thousands of pages and if they are not appropriately organized, the crawlers may overlook some of your most important content. For example:
- If you run a dog-walking business, you may have 100 blog posts about loosely relevant topics while only offering five key services. If there is no delineation between your primary services (which are most important to your domain), then search engines cannot determine the difference between a primary service like local dog walking and a blog post from five years ago about eco-friendly dog toys.
Sitemaps should also be designed to be user-facing. This allows a user to quickly identify the scope of content covered on your website and to navigate in a more robust way throughout it. Previous website users may remember your website name, but not the specific page they recently visited. Savvy internet users may return to your site and utilize the sitemap to find specific content they’re looking for.
How to Set Up Your Sitemap Using SEO Best Practices
Setting up a sitemap is likely much easier than you think. The first thing to do is review all existing content on your site and ensure the structure is sound. Starting from the homepage, look at your menu options and those links are most likely your first layer of organization for the sitemap. Some of these will require another layer of depth to segment content into more specific topics. However, there should never be more than three layers below the homepage for an SEO-friendly site structure. This means no page should require more than three clicks to navigate to from the homepage. It is important to recognize that you are creating a hierarchy of pages based on importance and how you want search engines to index them. So, keep in mind how you plan to monetize content on your site during this step.
For the XML file, four pieces of corresponding code are required for each URL. These include:
- Location
- Last changed
- Changed frequency
- Priority of page
You can use a text editor to simplify adding this code or if you are using WordPress, you can make updates to the XML file without code by downloading the Yoast SEO plugin and making changes to the SEO tab. Once the XML code properly reflects the structure of your website, you can validate that it was set up properly by using a sitemap validation tool. To put things into perspective, let’s take a look at a sitemap generated by Yoast SEO (a must if your site is built on WordPress):
Sitemap Last Modified
https://suncityadvising.com/post-sitemap.xml 2019-08-26 15:26 -07:00
https://suncityadvising.com/page-sitemap.xml 2019-08-26 14:29 -07:00
https://suncityadvising.com/category-sitemap.xml 2019-08-26 15:26 -07:00
https://suncityadvising.com/author-sitemap.xml 2019-08-27 10:32 -07:00
https://suncityadvising.com/geo-sitemap.xml 2017-11-02 20:38 +00:00
Each one of these are considered separate sitemaps with their own links and lists of content types within them. If you follow the top “post-sitemap.xml” link, then you will be directed to the list of blog posts, as shown below (these are only the top 5 lines out of hundreds).
URL Images Last Mod.
https://suncityadvising.com/click-through-rate/ 1 2019-08-13 10:53 -07:00
https://suncityadvising.com/press-kit/ 1 2019-08-13 10:57 -07:00
https://suncityadvising.com/how-to-advertise-on-pandora/ 1 2019-08-13 10:57 -07:00
https://suncityadvising.com/huffington-post-submissions/ 1 2019-08-13 10:58 -07:00
https://suncityadvising.com/google-maps-error/ 1 2019-08-13 10:59 -07:00
Now that if you have a valid sitemap using proper structure and XML code, add it to Google Search Console by heading to the crawl tab and then submitting the sitemap. After a few moments, all successful pages will be indexed and any pages with errors will become clear for you to adjust as needed. You can also submit the sitemap to any other search engine that allows webmasters to do so. The entire domain is now:
- Properly organized
- Efficiently catalogued
- Individual pages can be identified based on relevance and importance
Structuring a Robots.txt File
In many cases, websites owners may have individual pages or entire categories of pages that should not be indexed. This is achieved by adding “disallow” features to the sitemap. Instead of listing the pages you want search engines to avoid on the sitemap, another page is required.
- Using your primary domain and adding “/robots.txt” (i.e. com/robots.txt), you are creating a page that search crawlers can easily follow to identify any published pages that should not be indexed.
What to Expect From SunCity Advising’s Sitemap Professionals
Upon successful completion of your sitemap pages and robots.txt page, a clear change will begin to occur for your website. This change is primarily a highlight of each search engines ability to quickly sift through all content on your website and prioritize pages exactly the way you want them to. The result of this efficiency is higher search engine rankings for the pages that matter most to your business.
Sitemap implementation can differ based on many factors; this guide is not a one-size-fits-all. If you are having trouble setting up a fully functional website sitemap that is beneficial to SEO, then don’t fret. SunCity Advising can help you set up a website sitemap; contact us today for a free consultation.
Grayson Turley, SEO Specialist
Grayson Turley is an SEO specialist with an emphasis on local ranking and page speed optimization. With a background in both marketing and finance, Grayson has increased marketing ROI for many satisfied clients. SunCity Advising specializes in developing high performing websites, including services in SEO, paid media advertising, social media, email marketing and other digital marketing solutions.
Our Promise
We provide every client with a hands-on account manager that takes ownership in, and is held accountable for, the successful results of your growth strategy!
The SunCity Advising marketing team is much more than a digital marketing company — reach out to see why our clients trust our firm with all of their tough digital marketing decisions.
Contact Us
Address:
SunCity Advising
7924 Ivanhoe Ave. Suite 1
La Jolla, CA 92037
Marketing Contact:
Ivan Reed
(858) 859-0123
info@suncityadvising.com
Open Hours
Monday: 8:00am-8:00pm PST
Tuesday: 8:00am-8:00pm PST
Wednesday: 8:00am-8:00pm PST
Thursday: 8:00am-8:00pm PST
Friday: 8:00am-8:00pm PST
Saturday: 8:00am-4:00pm PST
Sunday: 12:00pm-4:00pm PST



